
This year our visual theme for each of the Industry Action Plans has been developed with a Te Ao Māori context in mind.
For the Retail & Distribution industry we lean into the symbolism of the Ngahere, the forest. This symbolises the variety and abundance of products available in retail.

The Retail & Distribution industry is one which offers a variety of pathways for kaimahi. The broadness of the industry means that it provides kaimahi with ample opportunities to progress, upskill, innovate, and adapt.
The industry will continue to form a key pillar of New Zealand’s economy and be the main place of employment for many New Zealanders. There is also an ongoing focus to build an inclusive workforce with an increased focus around diversity and cultural awareness. There will be more opportunities for people to work in or own their businesses built on Te Ao Māori values.
The retail industry in New Zealand is a vital sector of the economy, encompassing a diverse range of businesses, from small independent shops to large multinational retailers. The Retail & Distribution industry includes 42,000 retail businesses in New Zealand, with nearly half of these businesses being small businesses and sole traders which employ no staff.
The Retail & Distribution industry includes the wholesale and retail of a range of products and services from fuel, liquor and supermarket groceries to garden supplies, sports and camping equipment. This includes distribution and sales for both online and through traditional ‘brick and mortar’ premises.
The Retail & Distribution industry is pivotal to New Zealand and accounts for 6% of the country’s GDP. Retail stores provide essential goods and services, making them easily accessible to the public both in urban centres and in rural communities, whether it’s groceries, clothing, electronics, or household items. In addition to a wide range of customer-facing roles, there are an increasing number of back-office roles across the industry. The expansion of different retail channels and technologies also means that there are a suite of new jobs (IT/dark stores/online sales) in the industry.

The Retail & Distribution industry employs approximately 257,000 people. These workers are diverse, comprising individuals from various demographic backgrounds, including students, part-time workers, immigrants, and professionals seeking career advancement opportunities. Within the retail sector, workers occupy various roles such as sales associates, cashiers, store managers, merchandisers, buyers, and customer service representatives. These roles may vary in skill level and responsibility depending on the size and type of the retail establishment.
While some workers may enter the retail industry in entry-level positions, the scale of the industry means that there are many opportunities for career advancement and professional growth to a number of different roles. These include store management, merchandising, marketing, e-commerce, supply chain management, finance, and management. In addition to formal retail qualifications, many companies offer specific training and development programmes such as product knowledge, sales techniques, customer service, and leadership development.
Many ākonga in the Retail and Distribution industry may transition within and beyond the Service sector. This means by supporting the upskilling of ākonga in the industry in literacy and problem-solving skills, the industry to help the wider New Zealand workforce in their future transitions and career progression.
Most ākonga (learners) for Retail are enrolled in Level 2 qualifications, compared to those in Distribution where most are enrolled at Level 3. Industry insights suggest that there are ongoing skills shortages within the Retail and Distribution industry. Nevertheless, the uptake of formal training and the overall level of qualifications are low for the industry and continues to decline. There is an increasing desire from the industry for a shorter, sharper, stackable credentials which address their skills shortages more easily while fitting around people’s busy schedules. Topics discussed include communication, sales, problem-solving, and leadership.

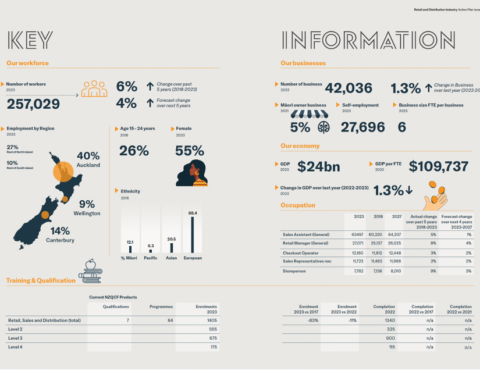
Explore Retail & Distribution industry workforce demographic, business, and economy statistics, and education and training data.
To help us get to the future state, we need to understand and tackle the challenges that the Retail & Distribution industry faces, while also seizing the opportunities that already exist or are on the horizon. These challenges are not new, as we have seen these continuing trends over recent years.






This information comes from the Supply Chain and Distribution National Industry Advisory Group (NIAG) held on 22 November 2023. The formation of the Supply Chain and Distribution NIAG is in direct response to industry need and NIAG members are able to provide their specialist perspective of the sector’s current and future workforce needs.






Productivity is built on decades of investment – in skills, knowledge, technology, and relationships. Productivity in business impacts a range of different areas including firm dynamics, technology diffusion, and innovation. Higher productivity improves wellbeing by increasing the nation’s incomes and our ability to produce and afford goods and services that underpin a happy, healthy life. Despite tough trading conditions, many retailers still seek staff with good sales and customer service skills. But training and upskilling are more difficult with limited resources – adding to the productivity challenge.
Online retail is having a huge impact on how consumers spend their time and money. Contactless payments and self-checkout are just some examples of how technology can be used to streamline and automate the shopping experience for customers. Retailers have to capitalise on new technology to ensure they keep up with these advances and behaviour changes. From digitising operations, e-commerce and digital marketing, there is a range of opportunities for retailers to explore.
Retailers can use artificial intelligence and analytics to identify and predict shoppers’ needs, trends and behaviour to create targeted campaigns for customers. Retailers can also employ mobile applications to reach more people and market to a wider audience. Ease of use and cost are key barriers to retailers adopting these digital solutions, however, these technological advances can help retailers to become more efficient, attract more customers and ultimately grow their businesses.
Technology such as facial recognition and security cameras can also support proactive response and early intervention of retail crime. Retail crime poses a significant threat to businesses across New Zealand. From shoplifting and fraud to vandalism and robberies, the repercussions of retail crime can be far-reaching, causing financial loss, having a detrimental impact on employee safety and morale. Retailers have already made a significant investment of around $1,138 million into such equipment and other crime prevention approaches, thereby investing in retail productivity.
Traditional approaches to the Distribution industry’s operations such as inventory, logistics, pricing, rebates, and network can be reimagined through the application of advanced analytics and technology innovations. Data, analytics, and artificial intelligence are business enablers. They can help provide distributors real-time insights into market trends, consumer demands, route mapping and potential supply chain disruptions. Through adopting new technology distributors can expand, capture new customer demand and promote product innovation.

There are approximately 28,900 Māori in the Retail & Distribution industry. This makes up around 13.5% of the industry overall. There are a growing number of Māori owned businesses in the Retail & Distribution industry. Currently there are around 900 Māori-owned businesses across the motu and this is expected to grow significantly over the coming years. In addition, there is an increase in demand for Māori products and Māori retailers, such as, clothing with Māori designs and emphasis on storytelling and authenticity when selling New Zealand products.
Workforce Development considerations that are particularly important to Māori include:
Leadership commitment to cultural capacity
Promote the necessity for a leadership commitment in driving cultural capability and acknowledging there are areas in which improvement is required.
Cultural education
Educate the workforce when it comes to celebration and significance of traditional events during the year.
Māori leadership qualities
Encourage a focus on the characteristics of strong Māori leaders, including being physically fit, emotionally intelligent, culturally aware, and posing good soft skills.
Learning initiatives
Encourage learning initiatives, including online courses in te reo and group learning sessions for cultural improvement.
Cultural obligations and authentic appreciation
Promote awareness of cultural obligations and the importance of leaders authentically appreciating and understanding different
cultures.

There are approximately 16,000 Pacific workers in Retail and Distribution roles, working across the motu. This is around 7% of the Retail and Distribution workforce which is reflective of a high proportion of Pacific workers employed in the service sector. It is important for industry to support Pacific workers current in the workforce to develop and grow into leadership and management positions.
Cultural awareness
Encourage leadership to promote the strengths of a culturally diverse work environment. Promote the strength of religious and family values within the Pacific communities. And how this has a positive effect on the community.
Balancing work and family
Encouraging recognition that family priorities may sometimes take precedence over work, potentially creating challenges. Encourage the importance of a supportive workplace culture, that is aware of family commitments.
Talent and recognition
Encourage leadership to identify talent and move towards upskilling quickly to build confidence in learners. Sometimes the learners are too humble to put their own hand up for recognition and opportunities.
Skill development initiatives
Promote funding to support with soft skills and English where needed. Encourage career progression and advancement into leadership roles.

Of the total 257,000 workers in the Retail and Distribution industry, around 2.5% are Tāngata Whaikaha.
Cultural awareness
Encourage leadership to promote the strengths of a culturally diverse work environment. Promote the strength of religious and family values within the Pacific communities. And how this has a positive effect on the community.
Balancing work and family
Encouraging recognition that family priorities may sometimes take precedence over work, potentially creating challenges. Encourage the importance of a supportive workplace culture, that is aware of family commitments.
Talent and recognition
Encourage leadership to identify talent and move towards upskilling quickly to build confidence in learners. Sometimes the learners are too humble to put their own hand up for recognition and opportunities.
Skill development initiatives
Promote funding to support with soft skills and English where needed. Encourage career progression and advancement into leadership roles.

Of the total 230,800 workers in the Retail and Distribution industry, approximately 58% are women.
Work-life balance
Emphasizing tailored work hours, potentially unlimited sick days, and flexible working hours to accommodate family responsibilities.
Inclusivity
Addressing the needs of women from different cultures, recognizing potential confidence barriers, and fostering a culture change towards more inclusive attitudes.
Team diversity
Highlighting the importance of having a balanced team with a mix of genders, acknowledging the unique strengths women bring to various roles.
Professional development
Creating clear professional pathways for women to access higher-level positions and encouraging training initiatives.
Leadership support
Ensuring leadership provides protection, safety, and encouragement for women in the workforce.
Diversity an advantage
Recognising the strength and advantages that come with a diverse workforce, including a different perspective, balance, and increased compassion.
Combatting unconscious bias
Acknowledging the role of women in keeping workplaces balanced and minimising unconscious bias.
Flexibility and adaptability
Appreciating women’s ability to excel in various roles, being flexible, and adapting to different job areas as needed.
Importance of role models
Highlighting the positive impact of having women in leadership positions, such as a Woman CEO, to inspire and set an example for others.
Communication and empathy
Recognising women’s strengths in customer service, communication, empathy, accuracy, and attention to detail.

A number of misconceptions have impacted people’s perceptions of retail as a career in New Zealand, with their daily retail experiences heavily shaping their view of the industry.
This is a central focus for the industry who are reporting that these perceptions are having an impact on their ability to recruit skilled workers. Retail is a broad sector with a huge range of roles and adventures to explore. However, for many in New Zealand, their view of retail is quite narrow. Retail NZ have done a research piece Retail NZ – Perceptions of Retail identifying the perceptions of retail and the knowledge gap discouraging people from joining the sector. This research on the perceptions of retail as a career covered a diverse range of the population including a survey of 2000 kiwis and retailers.
This research found that many view retail as:
Most people are not aware that the majority of retail roles are not on the shop floor and actually host a wide variety of roles and specialisations. As a result of this, many New Zealanders view retail as not high-status work and associate working in retail with lacking ambition or drive. Therefore, many young New Zealanders may worry about how they are viewed if they choose to work in retail or may face parental prejudice against a career in the sector.
Retail NZ have identified three major shifts which could help build more equity and status into the sector and priming core audiences so that when jobs become available, they are more likely to take the leap:
These shifts are focused on long-term growth and tackling deep-seated perceptions.

Transformational change in the Service sector workforce will take time, but to achieve that change, we need to start taking action now. This plan includes the key areas of focus, medium-term actions and short-term initiatives. These initiatives and actions can be thought of as individual threads that weave together to achieve workforce transformation.
To support progress with these actions, we have monitored what has been achieved in the last 12 months and what more will be delivered in future.
Download our actions and progress: